ProductsAll Products
.NET Components
DownloadsAll Downloads
There's only one layout algorithm that can produce a nice drawing of almost every kind of graph. This is the Orthogonal Graph Layout Algorithm. As you can expect its unmatched power and universality come with a price – it is very complex and extremely hard to implement. That's why Nevron is proud to present you the NOrthogonalGraphLayout class which implements the orthogonal graph drawing algorithm. An orthogonal drawing of a graph is an embedding in the plane such that all edges are drawn as sequences of horizontal and vertical segments. In particular for nonplanar and nonbiconnected planar graphs, this is a big improvement. The algorithm is complex and very hard to implement, but it is fast and handles both planar and nonplanar graphs at the same time.
Let G = (V; E) be a graph, n = |V|; m = |E|. A point where the drawing of an edge changes its direction is called a bend of this edge. If the drawing of an edge has at most k bends we call this edge k-bent. An orthogonal drawing is called an embedding in the rectangular grid if all vertices and bendpoints are drawn on integer coordinates.
Our algorithm takes as input a simple graph and produces an orthogonal grid drawing. Note that if the input graph is planar, the resulting drawing is also planar (i.e. without edge crossings). In the case of non-planar graphs the edge crossings are inevitable but the algorithm tries to keep their number as low as possible. For both planar and non-planar graphs the layout offers a great improvement in the readability of the graph by maintaining the following aesthetic criteria (given by their priority in descending order):
- minimal number of edge crossings (0 for planar graphs)
- minimal number of bends
- minimal area of the final drawing
When planarity testing is completed and the planar topology of the graph is determined, we must obtain the faces of the planar graph. The execution of the algorithm can be viewed as person walking along the edges of the graph, continuously choosing the rightmost option at every vertex.
An orthogonal drawing of a graph is an embedding in the plane such that all edges are drawn as sequences of horizontal and vertical segments. In particular for nonplanar and nonbiconnected planar graphs, this is a big improvement. The algorithm handles both planar and nonplanar graphs at the same time.
After building the orthogonal shape we perform a compaction step which deals with 2 important tasks: compaction of the total area of the drawing and bend minimization. Finally we calculate the coordinates of the vertices and edges of the grid drawing and render them using the Nevron Diagram Rendering Engine.
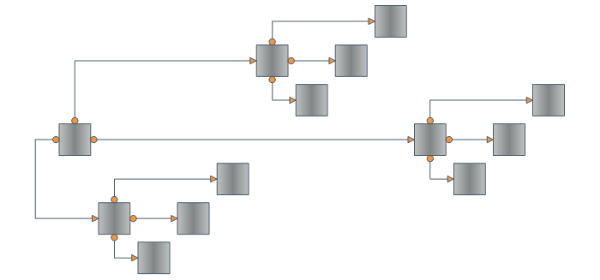
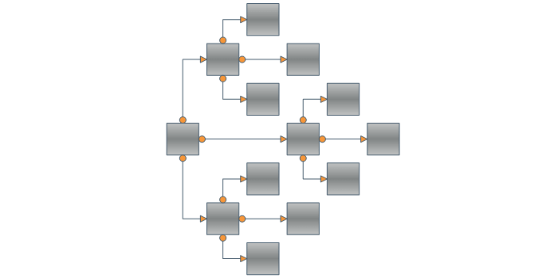
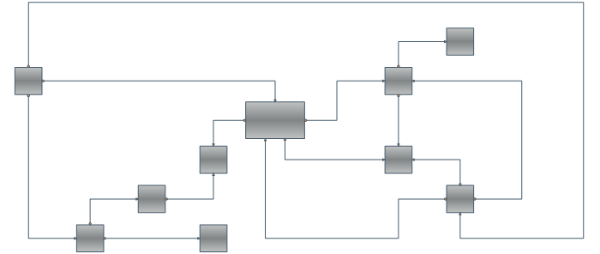
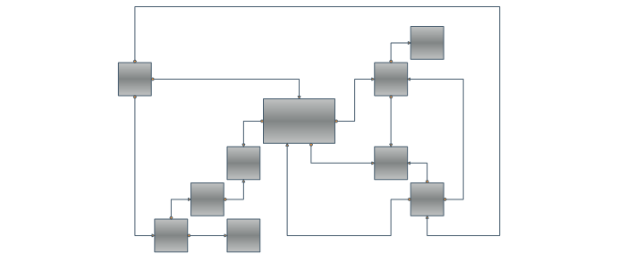
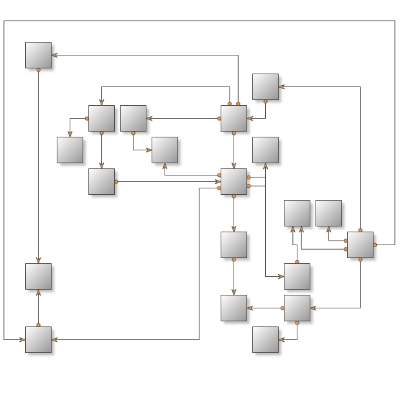
Besides the robust and highly optimized implementation of the Orthogonal Graph Layout, Nevron Diagram for .NET provides a dozen of other well implemented and carefully tested layout algorithms. If we take in mind all these layouts, the high number of examples and the detailed programmers’ documentation provided by Nevron, we may conclude that the professional visualization of complex graphs and diagrams has never been easier.
More information on Orthogonal Graph Layout is available in the Users Guide shipped with the fully-functional evaluation of the Diagram for .NET.